Submersible Pump

What is a Submersible Pump?
In industrial or agricultural projects where fluid pumping is required from depth, a water pump is needed that can be submerged in the fluid and perform pumping. A submersible pump is a multi-stage pump with an electric motor that uses a vertical centrifugal system to pump water or other liquids from deep wells.
A submersible pump is a type of centrifugal pump that operates similarly to multi-stage centrifugal pumps. It works by drawing fluid into the center of the impeller. The fluid is then forced outward by the impeller and into the next stage, increasing the pressure with each stage. The fluid is finally discharged from the outlet of the final stage. This process increases the kinetic energy of the water, which is then converted to pressure by the diffuser vanes. Typically, it does not require priming or initial startup because it is fully submerged in the fluid. The operation of a submersible pump is slightly different from a jet pump, as jet pumps transfer fluid by suction, while submersible pumps transfer fluid by pressure. Since this is a type of centrifugal pump, its operation is very similar to other types of centrifugal pumps.

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Pressure: 23.1 – 29.1 bar
- Body Material: Stainless steel
- Impeller Material: Noryl, stainless steel

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Head: 75.5 – 350 – 460 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Polycarbonate fiberglass, stainless steel 316, Noryl

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Head: 78 – 128 – 280 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Technopolymer

Features:
- Country of Origin: Japan
- Maximum Head: 75 – 492 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Stainless steel 304, technopolymer

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Pressure: 32 bar
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Technopolymer

Features:
- Country of Origin: China
- Maximum Head: 457 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Stainless steel 304 or Noryl

Features:
- Country of Origin: Iran
- Maximum Pressure: 30 bar
- Body Material: Cast iron
- Impeller Material: Cast iron

Features:
- Country of Origin: Iran
- Maximum Head: 72 – 110 meters
- Impeller Material: Stainless steel
- Applications: For transferring water from shallow wells, agricultural, industrial, and domestic uses

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Head: 75 – 322 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel 304
- Impeller Material: Noryl, technopolymer

Features:
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Maximum Head: 360 meters
- Body Material: Stainless steel
- Impeller Material: Stainless steel

Features:
- Country of Origin: China
- Maximum Head: 168 – 225 meters
- Applications: For transferring clean water from deep wells, tank circulation, cooling systems, water transfer in treatment plants, seawater transfer, etc.
Types of Deep Well Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps can be classified into four main categories based on their operating principle:
- Axial Flow or Propeller Submersible Pump: The name comes from the open impeller in its structure. Its operation is also similar to a turbine pump, with the difference being that in these pumps, the fluid exits the impeller parallel to the shaft. The application of this model is mainly in cases where high head with low flow rate is required.
- Turbine Submersible Pump: In these pumps, which are suitable for large water supply schemes or water intake from canals, rivers, and seas, the fluid path is parallel to the axis. This is evident from its vertical structure, and then it exits at an angle to it. For this reason, mixed flow impellers are used in these types of pumps. The main applications of this category can be summarized as follows:
- Pumping water from wells
- Suction pools
- Pumping stations
- Shaft Sleeve Submersible Pump: In shaft sleeve pumps, the fluid is first sent from the impeller to the outlet, which is a pipe around the shaft. An important point about this type of pump is that the fluid must have correct lubrication. Otherwise, the chamber and shaft are filled with a lubricant.
- Submersible Electropump: As the name suggests, the structure of these pumps uses an electric motor and a pump that is coupled and connected together. The water that enters this model cools the motor and lubricates the bearings. Its application is mainly in deep wells. Therefore, it is also called a deep well submersible water pump.
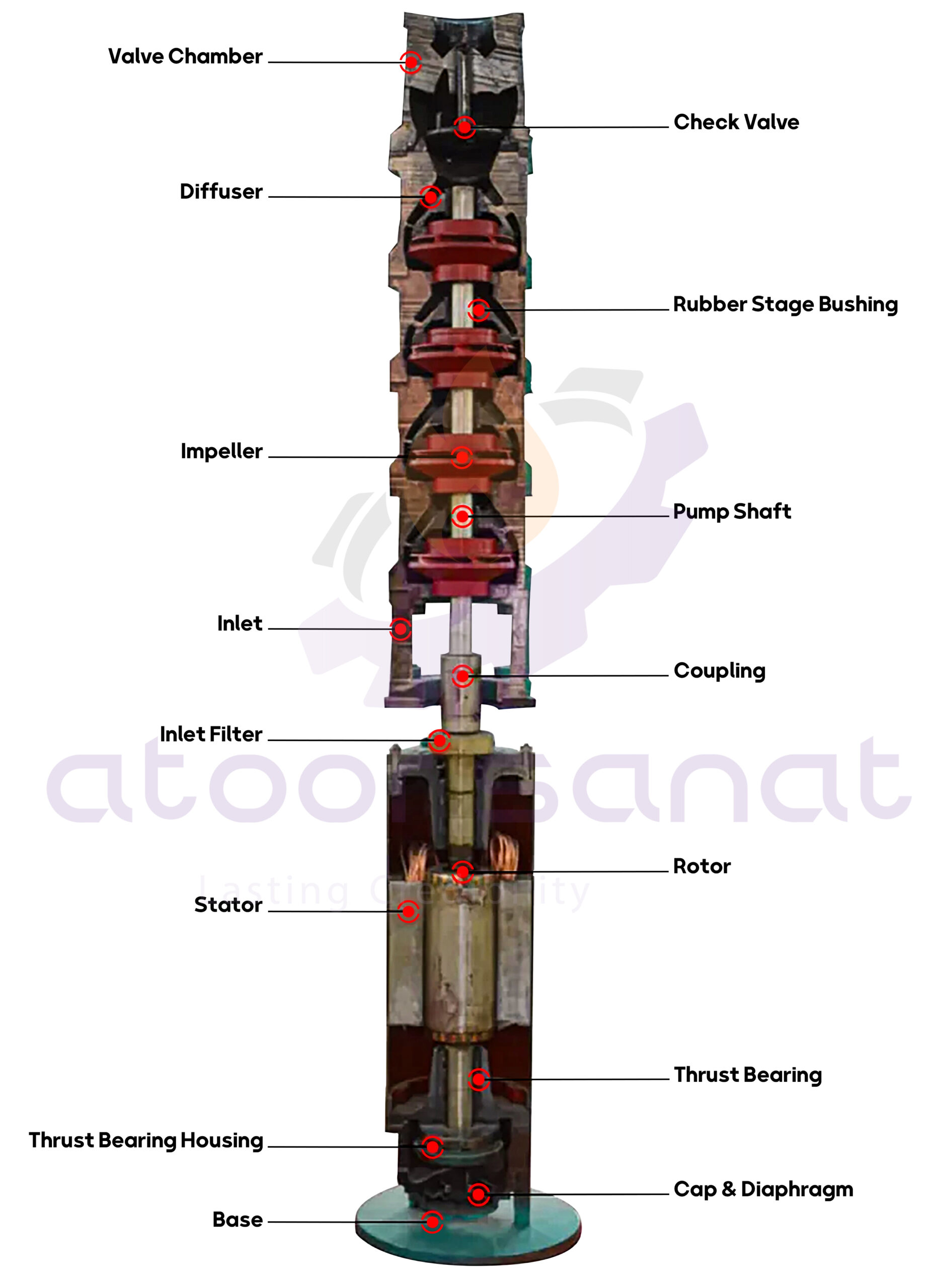
Components of a Submersible Pump
Stator:
The stator is a crucial component in the energy conversion of a submersible pump motor. Due to its stationary nature, it is named the stator. The stator consists of a casing, stator core, and stator windings. A three-phase alternating current is transmitted to the stator windings through a cable line, creating a rotating magnetic field in the stator core. The casing, through casting, steel rolling after welding processing, or direct processing by seamless steel tubes, strengthens the casing assembly, and ensures that the inner circle of the core body is highly concentric. This minimizes any friction between the stator and rotor.
The stator core is the motor’s guiding magnet. It is folded from silicon steel sheets using a die and fixed axially by a retaining ring. The inner circle of the iron core is provided with a groove for placement.
Rotor:
The rotor is also a critical component in the energy conversion of the submersible pump motor. The rotor current interacts with the rotating magnetic field of the stator, producing an electromagnetic torque that drives the motor to rotate. The rotor consists of a rotor core, a balance washer, and a rotating shaft.
The rotor core is the motor’s guiding magnet. It is folded from silicon steel sheets and pressed onto the rotating shaft. The core is fixed in both the axial and circumferential directions to prevent relative movement. Cast aluminum rotors often omit the key, and the iron core of the rotor is directly connected to the shaft due to the heat dissipation of the cast aluminum.
Motors with small capacities are mostly made of cast aluminum rotors, while larger capacity motors are mainly made of copper bands. Rotor parts rotate at high speeds, so the dynamic balance of the rotor must be corrected by the weight removal method to ensure good mechanical performance of the submersible motor and reduce vibration and noise. Generally, there is a balance washer on the rotor. The most common material for the rotating shaft of a submersible motor is 45 steel.
Air Gap:
The stator and rotor have a smaller but uniform air gap in the radial direction. The air gap has a significant impact on motor performance. A smaller air gap can be used to guide the current and improve the power factor. However, considering the manufacturing process level, the air gap of a small submersible pump is 0.5 to 0.8 mm, and the air gap of a medium-power submersible sewage pump is 0.8 to 4.1 mm. The air gap of a large-flow submersible pump is usually no more than 2 mm.
Bearings:
Small-power submersible pumps use two rolling bearings, with one thrust bearing. For medium power, a combination of rolling and thrust bearings is used. Large-power submersible pumps even use cylindrical rollers and a pair of conical rollers to bear the radial and axial forces. The lower bearing and rotating shaft should be clamped to prevent axial movement of the main shaft during operation. QS submersible pumps are often used for bearing guidance.
Seals or Watertight Seals:
To equip the submersible pump to prevent water from entering the motor, static and dynamic sealing is divided. Dynamic sealing is mainly created around the shaft. Static sealing of major components is often done by a sealing ring (O-Ring), and the cable outlet also has a static seal, which is often a screw type. For dynamic sealing, integrated seals, single-ended mechanical seals, double mechanical seals, labyrinth seals, or skeleton seals are commonly used. In most cases, graphite, ceramic, and carbide mechanical seals are used.
Wiring Cavities and Cables:
The submersible pump cable and motor windings must be stably connected in the wiring cavity. When ensuring that the motor does not vibrate, displace, and functions daily, the cable lead and motor windings will not be damaged. Cable connections should be made of polyethylene or PVC insulation and nylon sheath as mechanical protection. Terminals often connect cables and motor windings. The cable voltage is not less than the motor rated voltage, the current is not less than the motor rated current, and it should be selected according to the submersible pump, using the environment, temperature, pressure, corrosion, and other rational choices.
Impeller:
After the impeller rotates, the liquid is introduced by the blade, the pressure and speed increase, and the motor energy is transferred to the liquid. The impeller is generally made of different materials such as HT200 cast iron or stainless steel. For wear-resistant applications, you can use ZGlcrl3 cast steel, ductile iron, or high-chromium cast iron QT600-3. Copper alloy or stainless steel can be used for corrosion resistance.

