Motor Pump

Gasoline Water Pumps
A gasoline water pump is a portable water pump equipped with a driving engine, used in a variety of applications. It’s one of the most common types of pumps in agricultural applications and is widely used due to its low cost. The driving engine of this pump is an internal combustion engine fueled by gasoline, which can be two-stroke or four-stroke.
Gasoline water pumps are typically centrifugal pumps. These pumps are directly connected to the engine via a shaft. The engines used in these pumps usually have high power, and therefore these pumps can pump high flow rates.

Features:
- Country of Origin: Japan
- Maximum Head: 27 meters
- Applications: For sump pumping, drainage, rainwater harvesting, agricultural irrigation, and water source drainage.

Features:
- Country of Origin: China
- Maximum Head: 18 – 80 meters
- Body Material: Aluminum
- Impeller Material: Cast iron, stainless cast iron
How Does a Booster Pump Work?
Comparison of Gasoline and Electric Water Pumps
The most common types of pump drives are gasoline and electric motors; therefore, the first question when selecting a pump is which of these two types of pumps you need. Gasoline and electric motors have very different characteristics, making each suitable for use in a specific range of applications. Therefore, in the following, we will compare a gasoline engine with an electric motor so that you can easily choose the right pump for your application based on the specified characteristics.
1-Power
One of the biggest concerns users have about using pumps in different applications is the supply of the required power for the duration of the pump’s use. For high-power industrial applications such as pumping high-flow fluids and refineries, gasoline engines are more suitable because these engines can provide the high pressure required for these applications. This pressure can reach up to 500 bar in some of the mentioned applications. In other applications that require medium pressure, both gasoline and electric pumps have similar performance, and both types can be used.
2-Noise Level
The use of gasoline engines is not possible in applications where there are limitations on the maximum allowable noise level due to the high noise they produce. Due to having internal combustion engines and fuel explosions inside the cylinders, these pumps produce a high level of noise that is annoying. On the other hand, in many agricultural, industrial, and commercial applications, there is a very large space, and the presence of noise is not a criterion for selecting mechanical equipment, and therefore, gasoline pumps can be used in these applications.
3-Maintenance
Gasoline engines have many mechanical parts and require a lot of inspection and maintenance. Items such as oil level, cooling system, and other parts must be checked periodically to ensure smooth operation. In contrast, electric motors are closed devices that require much less maintenance.
4-Size and Application
Depending on your application, size and portability can be important criteria. If the size of the pumping system is important, gasoline pumps are not a good choice because these pumps, due to being accompanied by an internal combustion engine, have a large volume and require open space and air for cooling. In contrast, electric motors can be used in confined and small spaces. Gasoline engines can be easily moved and therefore, these engines are a suitable choice for applications such as commercial cleaning equipment. An important point to consider when using gasoline pumps is that these engines should not be used in enclosed spaces due to the emission of toxic gases.
5-Usage Time
A gasoline engine, depending on the fuel tank capacity, can have a longer usage time than an electric motor with a battery. Moreover, the fuel tank of a gasoline engine can be easily filled, but in mobile applications, charging the battery is more difficult and takes more time.
6-Price
In calculating the price of a motor pump, there are two main criteria. The first criterion is the initial cost or the price of the motor pump, and the second criterion is the ongoing costs. Because there are more parts and sections in gasoline engines, the price of these pumps is higher than pumps with electric motors, but the initial cost is only one of the selection criteria, and a decision cannot be made based on it alone. Market changes and events happening in the world can change these prices. Unlike gasoline engines, whose prices have decreased in recent decades, the price of electric motors has not changed much. The maintenance cost of gasoline pumps is generally higher, which should be considered in financial calculations.
Parts of a Gasoline Water Pump
Today, gasoline water pumps are designed and manufactured by many companies, and each of these companies implements its own specific technical knowledge in this field. Therefore, gasoline pumps have different features and parts, but in general, it can be said that these pumps have many common parts. The figure below shows the parts of a typical gasoline pump.
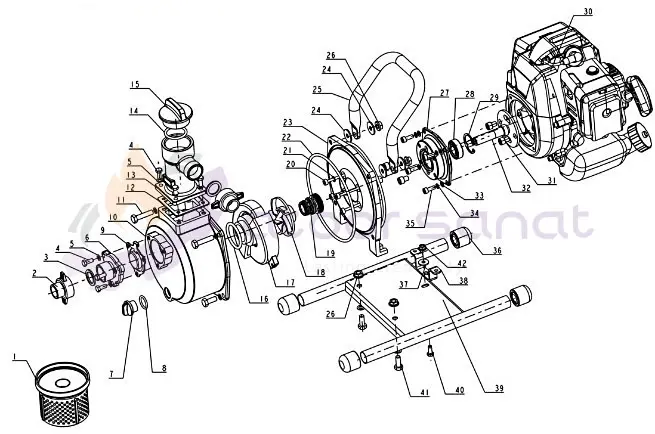
1 Water Filter
2 Fastening piece
3 Coupling seal washer
4 Hex bolt
5 Flat washer
6 Water inlet port
7 Plug
8 Seal ring
9 Seal ring, water inlet port
10 Casing
11 Hex bolt
12 Seal ring, water outlet port
13 Water outlet port
14 O Ring
15 End cap
16 Seal ring
17 Guide vane
18 Impeller
19 Mechanical seal
20 Inner hex screw
21 Aluminum spacer
22 Sealing Washer, casing cover
23 Casing cover
24 Big flat washer
25 Handle
26 Nut
27 Connecting Flange
28 Bearing
29 Circlip
30 Engine
31 Inner hex screw
32 shaft
33 Flat washer
34 Spring washer
35 Inner hex screw
36 Damping bushing
37 Big flat washer
38 Supporting bracket, engine
39 Frame
40 Flange bolt
41 Hex Bolt
42 Nut

