Pool Pump

Introduction to Pool Pumps
Swimming pool pumps are the primary component of a pool’s water filtration system. Without them, water filtration and pool use would not be possible. By circulating pool water, pool pumps distribute chemicals effectively throughout the pool. This not only sanitizes the water but also removes debris from the pool. In a pool filtration system, the pump plays a role similar to the heart in the human body. It pumps water throughout the pool and disperses chemicals and sanitizers. Depending on the pool’s volume, it is usually recommended to circulate the pool water daily. This can be achieved using a pool pump that is sized appropriately for the pool.

Features:
- Country of Origin: China
- Maximum Power: 10 HP
- Body and Base Material: Polypropylene
- Impeller Material: PPO
- Applications: Circulation of water in small household pools, filtering dirty water with suspended solids.
Specifications
The primary function of a pool pump is to circulate pool water and pass it through the filtration system. Pool pumps, which are a type of centrifugal or radial flow pump, are available in both Household and industrial grades. Their structure, as shown in the figure, consists of three main parts:
- Electric motor to provide kinetic energy to the impeller
- Strainer (with a plastic basket)
- Corrosion resistant impeller
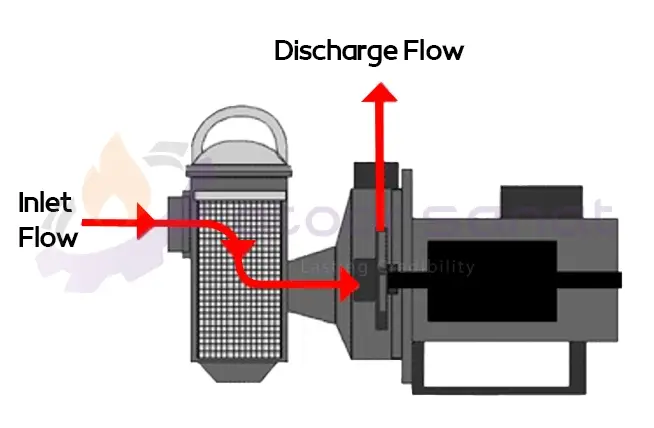
The pool pump motor operates on electricity and with a voltage of 110 or 220 volts. This electric motor is air-cooled. When using pool pumps, care must be taken to prevent excess water from entering the motor through the cooling vents located at the bottom of the housing. The pump impeller is attached to the end of the motor shaft.
The most significant difference between pool pumps and other types of pumps is the strainer used in the pump head. This is located in a large cylindrical section covered by a plastic lid. In this section, a plastic basket with a mesh wall manufactured with a specific mesh size forms the structure of the strainer.
How Pool Pumps Work
When the impeller starts, the pool water is drawn into the pump through the strainer and exits the pump through the pipe leading to the filter. The impeller has a small opening that can become clogged by debris. If you notice that the pressure on the gauge above the filter is lower than recommended and if the amount of water returning to the pool has decreased, the impeller may be clogged or damaged. To ensure that the impeller inlet is clean, the impeller must be removed and inspected closely.
The strainer installed in the pump head prevents debris in the pool from entering the impeller. Inside the strainer is a basket that should be cleaned every two weeks. If this basket is clogged, the flow of water into the pump will be restricted, and the pump will start to pump air instead of water. This can damage both the pump impeller and the housing. Also, if this basket were not present, the impeller could be clogged by particles and debris in the water, preventing water from being pumped and eventually damaging the impeller.
Internal and External Components of Pool Pumps
Pool pumps have a very simple design. Simply put, a pump is a device that can pump at least 80 gallons of water per minute. In practice, the components of pool pumps can be divided into two categories: internal components and external structure. The internal components are the parts that circulate the water, and the external structure prevents water leakage.
External Structure of Pool Pumps
As mentioned, the primary function of the external structure of pool pumps is to prevent water leakage. This part of the pump generally consists of five parts. In the following, we will examine the components of the external structure of pool pumps.
- Pump housing: The pump housing is actually the body of the pump, and all internal or external components of the pump, including the impeller, diffuser, and motor, are installed inside or on this housing. The pump housing is currently made of a type of impact-resistant composite called Noryl. This material is elastic, rustproof, and highly resistant to heat, rain, and water pressure.
- Strainer lid: The strainer lid is the main inspection point of the pump, allowing the repairman or pump owner to determine the health of the pump. Seeing large air bubbles or no water in the strainer lid when the pump is running may indicate air leaks along the suction line. For ease of inspection, the pump lid is made of a type of transparent glass called Lexan. Lexan is a material used to make bulletproof glass and other glass-like materials.
- Strainer basket: The strainer basket or filter basket separates debris before the water reaches the motor parts. This basket, by preventing the entry of hard particles such as gravel, prevents damage to the impeller and other drive components, thereby reducing pump maintenance costs.
- Gaskets and seals: Gaskets and seals are the components that prevent water from leaking out of the pump housing. The use of poor-quality gaskets can cause the equipment to get wet or the pump to fill with air instead of water. There are four gaskets and seals in pool pumps:
- Lid gasket, located under or over the strainer lid
- Diffuser gasket, located at the tip of the diffuser cone
- Housing gasket, which is the largest gasket in the pool pump and is located in the joint between the main housing and the seal plate.
- Shaft seal, which is a two-way mechanical seal located behind the impeller on the motor shaft. This seal is the most important seal in the pool pump, as it prevents water from entering the electric motor and causing damage.
- Seal plate: The seal plate is the main flange for installing the motor, allowing the motor to be securely fastened inside the housing. The reason for the name seal plate is that this plate holds the shaft to prevent water from leaking into the motor. This plate is also made of Noryl.
Internal Components of Pool Pumps
In addition to the external structure, pool pumps consist of internal components that are responsible for circulating and filtering water. In general, the internal components of pool pumps can be divided into three categories:
- Pump motor: The motor is the most important part of the pool pump, which produces the force necessary to rotate the pump impeller and circulate the water. The initial motors were designed for single-speed pumps, but with the increasing trend of using two-speed and variable-speed pumps, they have also been used for these types of pumps.
- Pump impeller: The impeller is the component that transfers the force transmitted from the electric motor by the rotating shaft to the fluid. The pump impeller is generally composed of two blades glued together. The front plate has an inlet that helps focus the impeller to direct water from the suction pipe.
- Pump diffuser: The diffuser is considered one of the accessories of the impeller and is of great importance. The diffuser, by creating a tight vacuum seal in the front chamber, strengthens the impeller so that the impeller power reaches its maximum. When the impeller starts moving, the diffuser envelope focuses the fluid transferred by the impeller, creating a Self-suicide condition.

